BIG-IP LTM VS: Packet Processing & Forwarding
|
Applied version
|
BIG-IP LTM VS: Packet Processing & Forwarding
About Full Proxy Architecture
In networking and web traffic, a proxy is a device or server that acts on behalf of other devices.
It sits between two the client and the server and performs a service.
Based on how it handles the connections, there are 2 types of proxies:
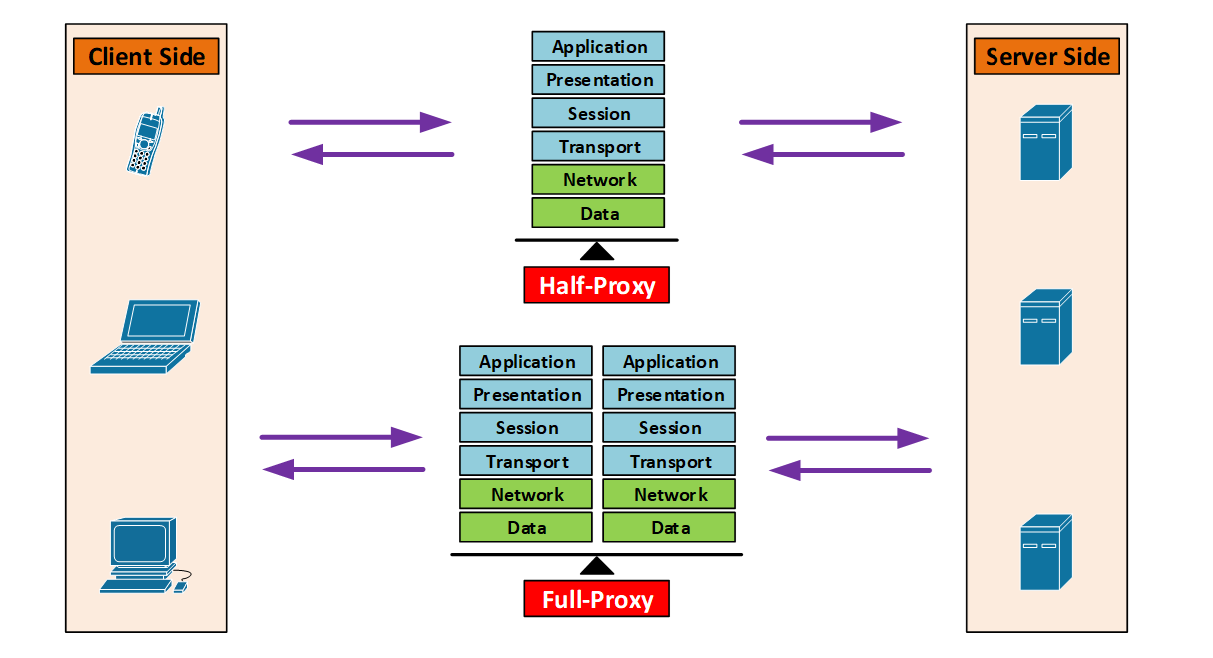
- Half-proxy: This type of proxy only maintain/handle 1 network stack between client and server for each connection
- Full-proxy: This type of proxy only maintain/handle 2 distinct network stacks between client and server for each connection
Half-Proxy vs. Full-Proxy
Half-Proxy
- Client connect to proxy, the proxy create a new entry in the connection table
- Proxy connect to the server using the same connection entry
- The proxy may do things like L4-based forwarding, IP Routing, NAT’ing
- Other than that there is nothing intelligent other than passing traffic
Full Proxy
- Client connect to proxy, the proxy create a new entry in the client-side connection table
- Proxy connect to the server, the proxy create a new entry in the server-side connection table
- TCP optimization: possible to have different TCP connection settings between client-side and server-side
- Examples: buffering, retransmits, TCP options, etc
- Full protocol visibility, traffic inspection, and enforce security policies
- Traffic manipulation: possible to manipulate the traffic in client-side and server-side
LTM Packet Flow
- 1-Armed Deployment Topology (Figure 1)
- 2-Armed Deployment Topology (Figure 2)
BIG-IP LTM packet flow requirement
- The rule that govern packet processing & forwarding stays the same.
- In terms of how packet processing & forwarding works, there is no different between which deployment topology do you choose.
- In most cases, to establish the connection successfully, the traffic flow need to be symmetrical
- Usually having different IP addresses between VS and Back-end server
- Problem with asymmetric traffic flow
- Client will not see any responses coming from Virtual Server IP address
- > Responses will be coming from back-end server IP address instead
- > Client will reject this kind of responses
- BIG-IP LTM won’t see any traffic (response) from pool member (back-end server)
- > 3-way-handshake will be failed
- > TCP segment out-of-order
- Any traffic alteration from BIG-IP LTM will also make it even worse
- > TCP Sequence Number will not match
- Client will not see any responses coming from Virtual Server IP address
- However for special cases and with right configuration, asymmetric traffic flow can be a successful scenario
- Stateless transparent proxy
- *Same IP address between VS and Back-end server
- nPath routing: DSR (Direct Server Return)
- *Different IP address between VS and Back-end server
- Stateless transparent proxy
LTM VS Address Translation
Local Traffic ›› Virtual Servers : Virtual Server List ›› VS properties ›› Configuration [Advanced]
BIG-IP LTM address translation
- Destination address translation: when receiving incoming traffic from clients, translates the IP address and/or port address of the VS into pool member IP address and/or port address. Examples:
- Dest. IP address translation, without dest. port address translation:
- > Client-side: Client 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to BIG-IP VS 200.123.123.123:443
- > Server-side: BIG-IP System 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to Back-end Server 192.168.123.11:443
- > 200.123.123.123 become 192.168.123.11
- Dest. IP address translation, with dest. port address translation:
- > Client-side: Client 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to BIG-IP VS 200.123.123.123:443
- > Server-side: BIG-IP System 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to Back-end Server 192.168.123.11:80
- > 200.123.123.123:443 become 192.168.123.11:80
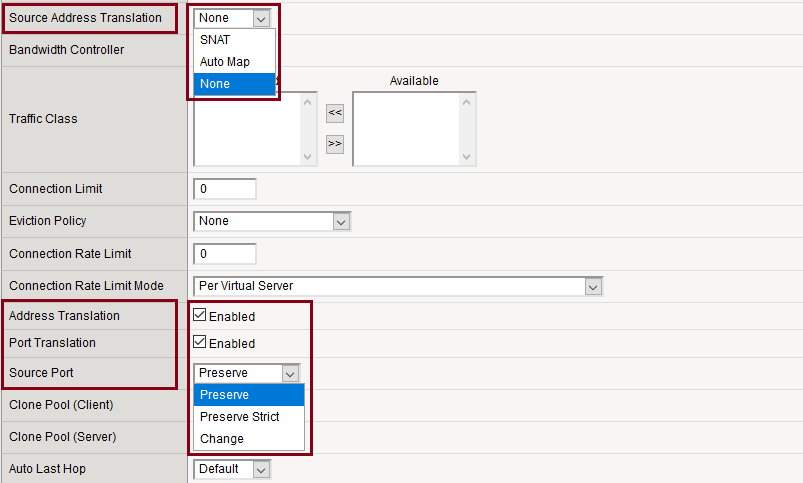
- Settings: under VS properties ›› Configuration [Advanced]
- > Address Translation: Enabled/Disabled
- > Port Translation: Enabled/Disabled
- Dest. IP address translation, without dest. port address translation:
- Source address translation: when receiving incoming traffic from clients, translates the IP address and/or port address of the client into another IP address and/or port address. Examples:
- Src. IP address translation, without src. port address translation:
- > Client-side: Client 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to BIG-IP VS 200.123.123.123:443
- > Server-side: BIG-IP System 192.168.123.245:52616 connect to Back-end Server 192.168.123.11:443
- > 27.123.200.123 become 192.168.123.245
- Src. IP address translation, with dest. port address translation:
- > Client-side: Client 27.123.200.123:52616 connect to BIG-IP VS 200.123.123.123:443
- > Server-side: BIG-IP System 192.168.123.245:53123 connect to Back-end Server 192.168.123.11:443
- > 27.123.200.123:52616 become 192.168.123.245:53123
- Settings: under VS properties ›› Configuration [Advanced]
- > Source Address Translation: SNAT (Snat Pool), Auto Map, None
- > Source Port: Preserve/Preserve Strict/Change
- Src. IP address translation, without src. port address translation:
*Note: Address translations are stateful, means the return traffic is already included/expected.
*Note: IP address translations are also achievable through “Local Traffic ›› Address Translation ›› SNAT/NAT”
0 Comments