ISAKMP IKE Phase 2 Details
(1) ISAKMP/IKE Phase 2
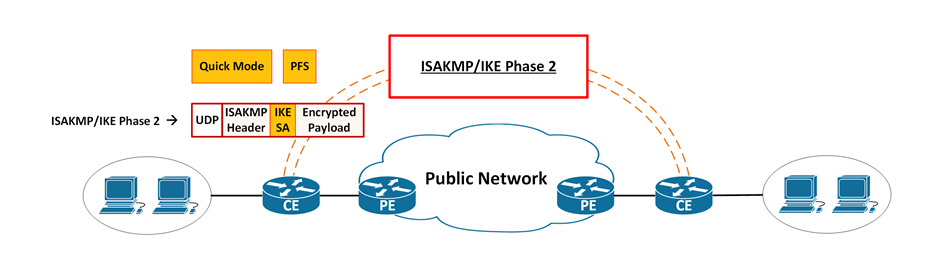
Phase 2
- Negotiates IPSec SA parameters protected by an existing IKE SA
- Establishes IPSec security associations
- Set up 2 unidirectional (1-way) secure tunnels for data connection
- Periodically renegotiates IPSec SAs to ensure security (when IPsec SA lifetime expires)
- Optionally performs an additional Diffie-Hellman exchange (when PFS is enabled)
*Phase-2 has 1 mode: Quick Mode, encrypted under IKE SA.
Quick Mode
- Quick mode has two exchanges (3 messages in total)
- All communication is secured by IKE SA
- It negotiates a shared IPSec policy, derives shared secret keying material used for the IPSec security algorithms, and establishes IPSec SAs
- The nonces are used to generate new shared secret key material and prevent replay attacks from generating bogus SAs
- Quick mode is also used to renegotiate a new IPSec SA when the IPSec SA lifetime expires.
- Base quick mode is used to refresh the keying material used to create the shared secret key
- Based on the keying material derived from the Diffie-Hellman exchange in phase 1.
- 1st exchange
- IPsec protocol (AH / ESP), mode of operation (Tunnel / Transport)
- Encryption algorithm, HMAC function, Proxy ACL, SA lifetime
- PFS capability, Diffie-Hellman key group
- (If PFS is enabled) Public key, nonces are sent for a Diffie-Hellman exchange
- 2nd exchange
- Message verification (hash payload)
- Anti replay and authentication protection
Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)
Secure communication protocols so previous key material isn’t related with current key generation.
ISAKMP/IKE provide PFS for both keys and all identities
- In IKE Phase 1
- Use “Main Mode” to protect the identities of crypto peers
- In IKE Phase 2
- Use “Quick Mode” to negotiate different security protocol protection
- Enable PFS option
- (Optionally) After IKE Phase 2 established, manually delete the IKE SA
PFS option in IKE Phase 2
- Quarantees that session keys are generated independently from previous session keys
- Prevent the attackers to use old session keys information to compromise the next session key
- Prevent the use of keying material derived from DH key exchange in Phase 1
- Instead of re-use the keying material derived from the previous DH exchange in Phase 1
- A new DH exchange is performed with each quick mode (initial handshake and the renegotiation)
- Provide keying material that has greater entropy
- Each Diffie-Hellman exchange requires large exponentiations, thereby increasing CPU use and exacting a performance cost.
- PFS requires IKE, doesn’t supported by manual keying
(2) Result of ISAKMP/IKE
Security Associations (SA)
Describes how two or more entities will utilize security services to communicate securely.
Maintain set of security components for secure communication, including:
- Encryption algorithm and symmetric key used
- Encryption algorithm and symmetric key used
- Lifetime of the SA
- Diffie-Hellman key group used
- (For IKE SA) Device authentication method used
- (For IPsec SA) IPsec protocol used
- Security Parameter Index
IPsec VPN has 2 unidirectional SAs
- Inbound SA: used by receiver to identify incoming IPsec packet
- Outbound SA: used by sender to tag the outgoing IPsec packet
Security Parameter Index (SPI)
An arbitrary value that is used by a receiver to identify the SA to which an incoming packet is bound
- IKE SA
- IKE header which always contains both SPIs
- Two 64-bit SPIs value
- Initiator SPI and responder SPI
- IPsec SA
- IPsec header contains only the sender’s outbound-SA SPI
- 32-bit SPI value
- Inbound-SA SPI and outbound-SA SPI
0 Comments