IPsec VPN Process
(1) IPsec VPN Control Plane
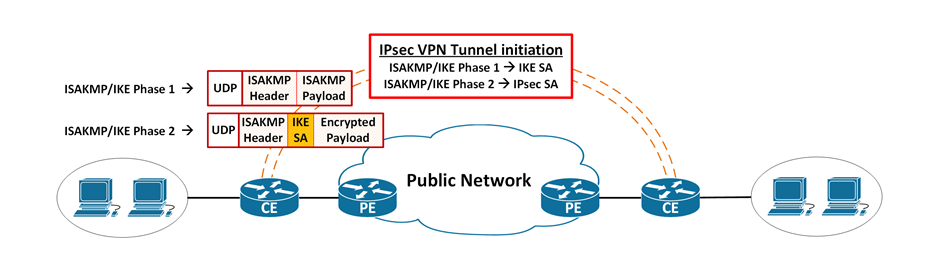
How to get router initiate the ISAKMP/IKE negotiation
Policy-based IPsec VPN
- Traffic routed to Crypto-enabled interface and matched by Crypto ACL
- Sometimes called “Interesting Traffic”
- E.g.: IPsec VPN Crypto Map based
Route-based IPsec VPN
- The SA is always on, not triggered-based
- E.g.: IPsec VPN with SVTI/DVTI
- For IPsec VPN with GRE
- Traffic routed to GRE interface trigger the negotiation
- Normally triggered by dynamic routing protocol control plane packets (hello)
IPsec VPN Control Plane Process
ISAKMP/IKE Phase-1 begins
- IPsec VPN client or gateway initiates a connection to remote VPN gateway
- Peers negotiate how the management connection will be protected
- Encryption cipher, Authentication hash algorithm, Peer authentication method, Lifetime duration, DH strength
- Diffie-Hellman is used to share the key material securely
- Generate & exchange nonce and DH public key
- Device authentication is performed
- Generate HASH payload using preshared key as part of calculation
- Authenticate the HASH payload
- Phase-1 SA or IKE SA is established
- (Optionally) User authentication is performed (XAUTH)
ISAKMP/IKE Phase-2 begins (protected by IKE SA)
- Peers negotiate how the data connection will be protected
- Encryption cipher, Authentication hash algorithm, Peer authentication method, Lifetime duration, PFS/DH strength
- (If PFS is on) Diffie-Hellman is used to share the key material securely
- Generate & exchange nonce and DH public key
- Phase-2 SA or IPsec SA is established
- Eventually the management and data connection will expire and will have to be rebuilt
ISAKMP/IKE packets
- Use UDP port 500 for both source and destination
- If NAT device is detected, use UDP port 4500 for both source and destination
- For remote-access IPsec VPN, there is an option to use TCP
- cTCP / IPsec over TCP / TCP traversal
(2) IPsec VPN Data Plane
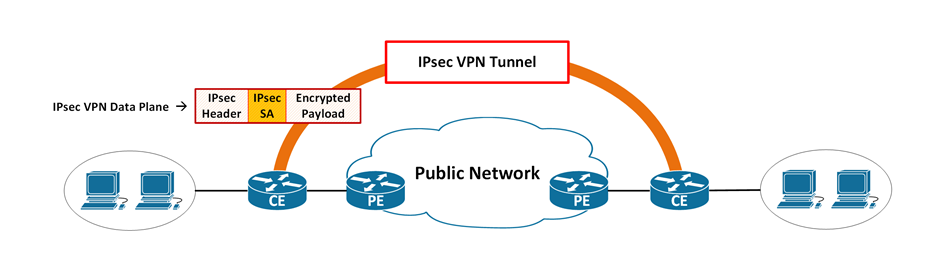
How to get traffic protected by IPsec SA
Policy-based IPsec VPN
- Traffic routed to Crypto-enabled interface and matched by Crypto ACL
- Doesn’t support dynamic routing protocol
- E.g.: IPsec VPN Crypto Map based
Route-based IPsec VPN
- Traffic routed to IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface
- Support dynamic routing protocol
- E.g.: IPsec VPN with GRE, IPsec VPN with SVTI/DVTI
IPsec VPN Data Plane
Data Encapsulation
Data payload is being encapsulated with IPsec protocol.
- Authentication header (AH)
- Use IP protocol number 50
- Doesn’t support data encryption and behind NAT deployment
- Encapsulation security payload (ESP)
- Use IP protocol number 51
- If behind NAT, use UDP port 4500 for both source and destination
- For remote-access IPsec VPN, there is an option to use TCP
- cTCP / IPsec over TCP / TCP traversal
*(If using Tunnel mode) Additional outer IP header is added
Data Encryption
IPsec payload is being encrypted with encypt-session-key and encryption algorithm
- DES (56-bit) encryption
- 3DES (168-bit) encryption
- AES (up to 256-bit) encryption
Data Authentication
IPsec-encrypted payload is being authenticated with auth-session-key and authentication algorithm
- HMAC-MD5 (96-bit) hash
- HMAC-SHA (up to 512-bit) hash
*HMAC is a variant that provides an additional level of hashing
0 Comments