IKE Keying And Authentication
(1) IKE Phase 1 Main Mode Keying
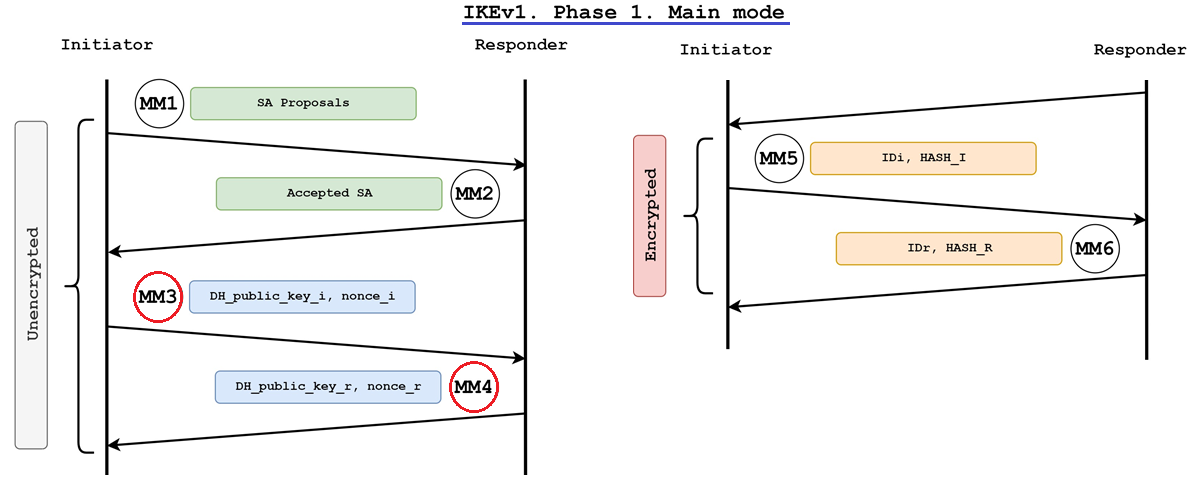
3rd message (from initiator), and 4th message (from responder) contains:
- Nonce
- “N = Number” “once = used only once”
- Randomly generated huge number, typically used in key generation
- DH public keys
- Used to generate “DH shared secret”
Seed Value (SKEYID), used to generate “Session Keys”
- For pre-shared keys = PRF ( pre-shared-key, Ni_b | Nr_b )
- For signatures: SKEYID = PRF ( Ni_b | Nr_b, g^xy )
- For public key encryption: SKEYID = PRF ( hash(Ni_b | Nr_b), CKY-I | CKY-R )
- Descriptions
- pre-shared-key: Local configured Preshared key
- PRF : Pseudo Random Function (similar to hash)
- Ni_b : initiator’s Nonce
- Nr_b : responder’s Nonce
(3x) Session Keys = SKEYID + DH shared secret
- (1st) Derivative Key: handed over to Phase 2 to generate its own “Session Keys”
- If PFS is not in used
- SKEYID_d = prf(SKEYID, g^xy | CKY-I | CKY-R | 0)
- (2nd) Authentication Key: used in Phase 1 in its data authentication (HMAC)
- SKEYID_a = prf(SKEYID, SKEYID_d | g^xy | CKY-I | CKY-R | 1)
- (3rd) Encryption Key: used in Phase 1 to do it’s symmetric encryption (DES, 3DES, AES)
- SKEYID_e = prf(SKEYID, SKEYID_a | g^xy | CKY-I | CKY-R | 2)
(2) IKE Authentication
IKE Phase 1 Main Mode peer authentication
IKE peer authentication methods:
- Preshared keys (ASCII alphanumeric characters)
- RSA signatures (Digital certificates using RSA algorithms)
- DSS signatures (Digital certificates using DSS algorithms)
- RSA encrypted nonces (RSA Public keys without Digital certificates)
- Revised encryption with RSA (RFC2409 section 5.3)
In order to authenticate IKE peer, both endpoint exchange “IKE identity” and “Hash data”
- Hash data generated by Initiator
- HASH_I = PRF (SKEYID, g^xi | g^xr | CKY-I | CKY-R | SAi_b | IDii_b )
- Hash data generated by Responder
- HASH_R = PRF (SKEYID, g^xr | g^xi | CKY-R | CKY-I | SAi_b | IDir_b )
- For authentication with either RSA encrypted nonces or pre-shared keys
- HASH_I and HASH_R directly authenticate the exchange.
- For authentication with digital signatures
- HASH_I and HASH_R are signed and verified
5th message and 6th message are encrypted with session key (but the header is clear text)
- IKE identity
- ID type: IPV4_ADDR (1)
- Protocol ID: 17
- Port: 500
- ID data: ID_IPV4_ADDR: 10.0.12.12
- Hash data (if using “Preshared key” or “RSA encrypted nonces“)
- Hash of entire “IKE identity”
- To verify / authenticate IKE peer identity
- Authentication success if each party able to compute the same Hash data from IKE identity
- Encrypted nonce & RSA public key (if using RSA encrypted nonces)
- Authentication success if each party able to decrypts the nonce and use it to compute and verify Hash data
- Digital certificate of IKE endpoint (if using “RSA certificate auth“)
- Peer’s Digital certificate is verified using CA public key (inside trusted root CA certificate)
- Peer’s RSA public key is contained inside Digital certificate
- This Digital certificate provides a level of assurance that a peer’s identity
- Digital signature of Hash data (if using “RSA certificate auth“)
- IKE identity will use FQDN as ID type
- This Digital signature is encrypted using peer’s RSA private key
- Authentication success if each party able to decrypt and verify Digital signature using peer’s RSA public key
IKE with RSA signatures authentication
Digital certificates using RSA algorithms, provide nonrepudiation (traceable) for the IKE negotiation.
How does it works:
- During IKE negotiations, peers exchange Digital certificate and Digital signature.
- Digital certificate is verified using CA public key
- Digital signature is verified using peer’s public key
- Authentication success if each party able to decrypt and verify Digital signature using peer’s RSA public key
Key steps to enable RSA signature authentication:
- Generating a RSA (private/public) key pair
#hostname branch1
#ip domain-name docisco.com
#crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 label BRANCH_KEY
#show crypto key BRANCH_KEY rsa - Define trusted CA server as a trustpoint for enrollment in VPN endpoint
#crypto pki trustpoint WIN2003
#enrollment url http://10.10.10.3/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll
#enrollment mode ra (WIN2003 Registration Authority)
#rsakeypair BRANCH_KEY
#revocation-check none - Obtaining and installing (trusting) a root CA certificate
#ntp server 10.10.10.10
#show clock
#crypto pki authenticate WIN2003
#debug crypto pki server - Online CA signed certificate enrollment
#crypto pki enroll WIN2003
% Create a challenge password (for revocation)
% FQDN? Subject Name? Include IP address?
Request certificate from CA
#show crypto <ca|pki> certificates - Manual CA signed certificate enrollment through TFTP
#crypto pki import WIN2003 pem url tftp://10.10.10.3/certsrv/msca <password>
% Importing CA certificate (tftp://10.10.10.3/certsrv/msca.ca)
% Importing private key PEM file (tftp://10.10.10.3/certsrv/msca.prv)
% Importing certificate PEM file (tftp://10.10.10.3/certsrv/msca.crt)
#show crypto <ca|pki> certificates - Use RSA signatures as Crypto peer authentication
#crypto isakmp policy 10
#authentication rsa-sig
IKE with RSA encrypted nonces authentication
RSA Public keys without Digital certificates, provide repudiation (untraceable) for the IKE negotiation.
How does it works:
- During IKE negotiations, peers exchange RSA public keys to authenticate each other’s IKE identity.
- Each party generate a nonce and encrypt it using peer’s RSA public key
- Authentication success if each party able to decrypts the nonce and use it to compute and verify Hash data
Key steps to enable RSA encrypted nonces authentication:
- Generating a RSA (private/public) key pair
#hostname branch1
#ip domain-name docisco.com
#crypto key generate rsa usage-keys modulus 1024 - Register / install remote’s RSA public key
#crypto key pubkey-chain rsa
#named-key branch2.docisco.com (or) #addressed-key 10.1.1.2 encryption
#address 10.1.1.2
#key-string
#0302017 4A7D385B 1234EF29 335FC973
#2DD50A37 C4F4B0FD 9DADE748 429618D5
#18242BA3 2EDFBDD3 4296142A DDF7D3D8
#08407685 2F2190A0 0B43F1BD 9A8A26DB
#07953829 791FCDE9 A98420F0 6A82045B
#990288A26 DBC64468 7789F76E EE21
#show crypto key pubkey-chain rsa - Use RSA signatures as Crypto peer authentication
#crypto isakmp policy 10
#authentication rsa-encr
0 Comments