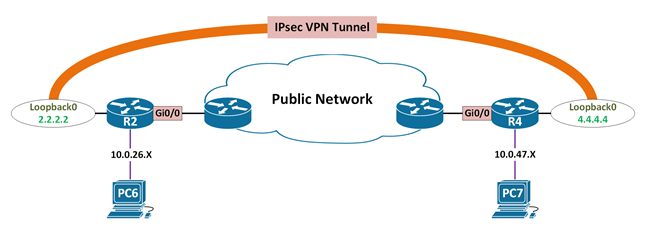
IPsec VPN With Manual Keying Overview
Manual Keying background
- Typical IPsec VPN Deployment relies on IKE/ISAKMP to establish a secure channel
- This secure channel is used to exchange and negotiate security parameters when building IPsec SAs
- One of the parameters is the “Shared Secret Keys” (also referred to as “Session Keys”)
- In instances in which IKE is unavailable, manual keying can be used.
- Such instances would include deploying IPsec VPN to another vendor endpoint that doesn’t support IKE
Disadvantages of using manual keying
- It doesn’t scale well due to the exponential increase in administrative overhead
- Key must be defined manually
- It doesn’t support the use of SA lifetime
- Key must be refreshed manually
- It doesn’t support anti replay protection
- It doesn’t support the use of CA (Certificate Authority)
- Only supported by IPsec VPN crypto map based
- It isn’t supported by many hardware-based VPN accelerators
How manual keying works:
- Instead of IKE/ISAKMP, IPsec-manual mode is used
- Session keys are manually inputted on both peers, each peer require:
- Inbound IPsec SA
- Outbound IPsec SA
- Both Inbound SA & Outbound SA require:
- Cipher key: session key for data encryption
- Authenticator key: session key for data integrity authentication
Session keys compatibility
Key specification
- Keys are in hexadecimal format
- Keys (bit) length must be compatible with the algorithm that being used
- Cipher key must match the encryption algorithm (DES/3DES/AES)
- Authenticator key must match the hash algorithm (MD5/SHA)
- Both inbound and outbound keys
- Within local device, they don’t have to match one another
- Within peer device, they have to match one another in tail & head direction
Manual key example
Both Peers are using the same algorithms
- DES Encryption, required 56-bit or 14 hexadecimal characters
- MD5 Authentication, required 128-bit or 32 hexadecimal characters
Peer-A
- Inbound cipher key = 1234567890abcd
- Outbound cipher key = dcba0987654321
- Inbound authenticator key = aaaaaaaabbbbbbbbccccccccdddddddd
- Inbound authenticator key = 11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff
Peer-B
- Inbound cipher key = dcba0987654321
- Outbound cipher key = 1234567890abcd
- Inbound authenticator key = 11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff
- Inbound authenticator key = aaaaaaaabbbbbbbbccccccccdddddddd
0 Comments