IPsec VPN Fragmentation Problem
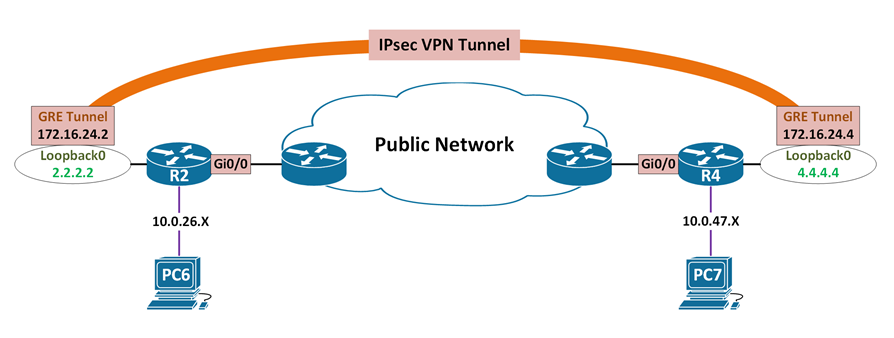
GRE over IPsec fragmentation problem
- IPsec plaintext MTU (inside IPsec SA) is not reliable
- IPsec plaintext MTU is 1466 bytes, but real plaintext IP MTU is 1442 bytes
- GRE IP MTU (1476 bytes) is not synced with IPsec plaintext MTU
- DF bit isn’t copied between headers
- PMTUD is broken between end host
- Router must encrypt, then fragment
- Fragmentation is typically done in software
- Spike the router’s CPU, and lower the throughput
Solution: Offload fragmentation to the end host
- Tune the tunnel IP MTU to fix PMTUD between end host
- Lower IP MTU on GRE interface to account for ESP overhead
- Actual overhead varies based on crypto algorithm
- Good rule of thumb is 1400 bytes for normal IP MTU, and 9000 bytes for jumbo IP MTU
- Implement Tunnel PMTUD for auto tunnel IP MTU
- #tunnel path-mtu-discovery
- #show interfaces tunnel24 | include Path
- “Path MTU Discovery (..) MTU 1442”
- DF bit is copied between headers
- Implement IPsec VTI for auto tunnel IP MTU
- #show crypto ipsec sa | include mtu
- IPsec plaintext MTU is reliable
- #show ip interfaces tunnel24 | include MTU
- GRE IP MTU is synced with IPsec plaintext MTU
- If end host doesn’t support PMTUD
- Adjust TCP MSS on GRE interface “GRE IP MTU – 20 bytes (IP) – 20 bytes (TCP)”
- For non-TCP traffic, we need to adjust the IP MTU on the end host directly
Tune IP MTU and TCP MSS
| !! R2 !! | !! R4 !! |
|
! Tunnel Interface interface Tunnel24 ip address 172.16.24.2 255.255.255.0 tunnel source 2.2.2.2 tunnel destination 4.4.4.4 tunnel mode gre ip ip mtu 1400 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 |
! Tunnel Interface interface Tunnel24 ip address 172.16.24.4 255.255.255.0 tunnel source 4.4.4.4 tunnel destination 2.2.2.2 tunnel mode gre ip ip mtu 1400 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 |
0 Comments